Summary:
Human reproduction is a complex process involving the male and female reproductive systems. The male reproductive system consists of the testes, vas deferens, seminal vesicles, prostate gland, and penis. The testes produce sperm and secrete the hormone testosterone, which regulates male reproductive functions. The female reproductive system includes the ovaries, fallopian tubes, uterus, and vagina. The ovaries produce eggs and secrete hormones like estrogen and progesterone.

Class 12 Biology Chapter 3 Human Reproduction book 📚 download in PDF format 👇👇
The process of gametogenesis involves the formation of male and female gametes—spermatogenesis in males and oogenesis in females. Fertilization occurs in the fallopian tube when a sperm cell fuses with an egg, forming a zygote. The zygote undergoes mitotic divisions, leading to the formation of a blastocyst, which implants in the uterine wall, initiating pregnancy.
Hormonal regulation plays a crucial role in reproduction. In females, the menstrual cycle is governed by hormones like FSH, LH, estrogen, and progesterone, which regulate ovulation and prepare the uterus for implantation. In males, FSH and LH regulate spermatogenesis and testosterone production.
Pregnancy and embryonic development involve the formation of the placenta, which facilitates nutrient and gas exchange between the mother and fetus. The chapter also touches upon parturition (childbirth) and lactation, highlighting the role of oxytocin and prolactin in these processes.
Understanding human reproduction is essential for grasping the biological basis of human development and the factors influencing fertility, pregnancy, and childbirth. This knowledge is fundamental for reproductive health and family planning.
Short Answer Questions:
What are the primary functions of the testes in the male reproductive system?
- The primary functions of the testes are to produce sperm through spermatogenesis and to secrete the hormone testosterone, which is essential for the development of male secondary sexual characteristics and the regulation of male reproductive functions.
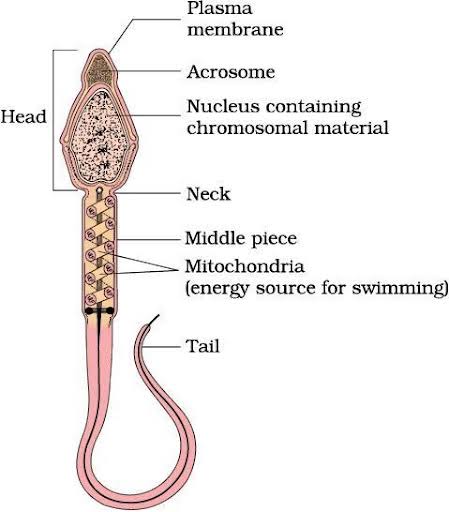
Describe the structure of a mature sperm.
- A mature sperm consists of three main parts: the head, which contains the nucleus and acrosome; the midpiece, packed with mitochondria to provide energy for movement; and the tail, a flagellum that propels the sperm toward the egg.
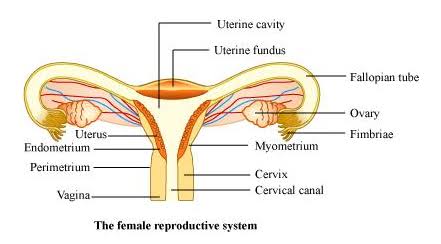
What is the role of the fallopian tubes in female reproduction?
- The fallopian tubes transport the ovulated egg from the ovary to the uterus. Fertilization typically occurs in the ampulla of the fallopian tube, where the sperm meets and fertilizes the egg.
Define oogenesis and where it occurs.
- Oogenesis is the process of egg formation in females. It occurs in the ovaries and involves the maturation of oogonia into primary oocytes, which eventually develop into mature ova (eggs) after meiosis.
What is the significance of the menstrual cycle?
- The menstrual cycle is crucial for preparing the female body for potential pregnancy. It involves the cyclic buildup and shedding of the uterine lining, regulated by hormonal changes, which allows for the possibility of fertilization and implantation.
Explain the phases of the menstrual cycle.
- The menstrual cycle has four phases: the menstrual phase (shedding of the uterine lining), the follicular phase (growth of follicles and uterine lining), ovulation (release of an egg), and the luteal phase (preparation of the uterus for implantation).
What happens during ovulation?
- During ovulation, a mature follicle ruptures, releasing a secondary oocyte into the fallopian tube. This event is triggered by a surge in luteinizing hormone (LH) and typically occurs around the 14th day of a 28-day menstrual cycle.
Describe the process of fertilization.
- Fertilization occurs when a sperm penetrates the egg’s outer layer, leading to the fusion of their nuclei. This results in the formation of a diploid zygote, which will undergo cell division to develop into an embryo.
What is a blastocyst?
- A blastocyst is an early-stage embryo that forms approximately five days after fertilization. It consists of an inner cell mass, which will develop into the fetus, and an outer layer called the trophoblast, which will contribute to the placenta.
How does implantation occur?
- Implantation occurs when the blastocyst attaches to the uterine wall, embedding itself into the endometrium. This process is crucial for establishing a connection between the mother and the developing embryo.
What is the role of the placenta?
- The placenta facilitates the exchange of nutrients, oxygen, and waste products between the mother and the fetus. It also produces hormones that support pregnancy, such as human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG).
Explain the significance of hCG during pregnancy.
- Human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) is produced by the placenta after implantation. It supports the corpus luteum, which secretes progesterone to maintain the uterine lining and prevent menstruation during pregnancy.
What is the difference between embryonic and fetal development?
- Embryonic development refers to the early stages of development from fertilization to the eighth week, during which the basic structures of the body form. Fetal development begins after the eighth week and involves the growth and maturation of these structures.
Describe the process of labor.
- Labor is the process of childbirth, involving regular contractions of the uterus that lead to the dilation of the cervix, delivery of the baby, and expulsion of the placenta. It occurs in three stages: dilation, expulsion, and placental delivery.
What are assisted reproductive technologies (ART)?
- Assisted reproductive technologies (ART) include medical procedures like in vitro fertilization (IVF) that help couples with infertility issues to conceive by manipulating eggs, sperm, or embryos outside the body.
Long Answer Questions
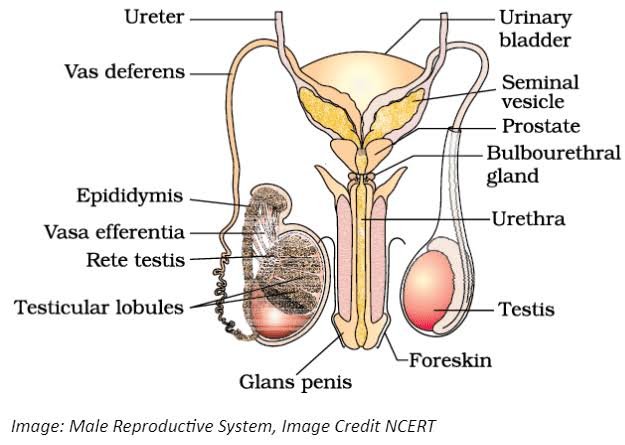
Describe the structure and function of the male reproductive system.
- The male reproductive system comprises external organs, such as the penis and scrotum, and internal organs, including the testes, vas deferens, seminal vesicles, prostate gland, and urethra. The testes produce sperm and testosterone. The vas deferens transports sperm from the testes to the urethra, where it is mixed with seminal fluid from the seminal vesicles and prostate gland to form semen. During ejaculation, semen is expelled through the urethra and penis.
Explain the hormonal regulation of the female menstrual cycle.
- The menstrual cycle is regulated by a complex interaction of hormones. The hypothalamus releases gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH), which stimulates the pituitary gland to secrete follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH). FSH promotes the growth of ovarian follicles, while LH triggers ovulation. Estrogen and progesterone, produced by the ovaries, regulate the growth and shedding of the uterine lining.
Discuss the stages of embryonic development after fertilization.
- After fertilization, the zygote undergoes cleavage, forming a morula. The morula develops into a blastocyst, which implants into the uterine wall. The inner cell mass of the blastocyst differentiates into the three germ layers—ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm—that give rise to all tissues and organs. This is followed by the formation of the amniotic sac, placenta, and umbilical cord, supporting the embryo’s development into a fetus.
How does the process of spermatogenesis differ from oogenesis?
- Spermatogenesis occurs in the testes and involves the continuous production of sperm throughout a male’s life, beginning at puberty. It results in four viable sperm from each spermatogonium. Oogenesis, on the other hand, occurs in the ovaries and is a cyclical process that begins before birth but is completed only upon fertilization. It produces one viable ovum and polar bodies from each oogonium.
What are the key differences between natural fertilization and in vitro fertilization (IVF)?
- Natural fertilization occurs within the female body, typically in the fallopian tubes, where sperm meets the egg. In vitro fertilization (IVF) involves extracting eggs and sperm, fertilizing them outside the body in a lab, and implanting the resulting embryo into the uterus. IVF is used when natural fertilization is not possible or has failed due to various infertility issues.
Describe the role of the corpus luteum in the menstrual cycle and pregnancy.
- The corpus luteum is formed from the ruptured follicle after ovulation. It secretes progesterone, which thickens the uterine lining to prepare for potential implantation. If pregnancy occurs, the corpus luteum continues to produce progesterone until the placenta takes over this role. If pregnancy does not occur, the corpus luteum degenerates, leading to a drop in progesterone and the onset of menstruation.
Explain the physiological changes that occur in a woman’s body during pregnancy.
- During pregnancy, a woman’s body undergoes numerous changes, including increased blood volume, weight gain, breast enlargement, and hormonal fluctuations. The uterus expands to accommodate the growing fetus, and the placenta develops to nourish the baby. There are also changes in the cardiovascular, respiratory, and digestive systems to support the increased demands of pregnancy.
What is the significance of the amniotic sac and amniotic fluid in fetal development?
- The amniotic sac, filled with amniotic fluid, surrounds and protects the developing fetus. The fluid acts as a cushion, absorbing shocks and allowing the fetus to move freely, which is essential for muscle and bone development. The amniotic fluid also maintains a constant temperature and prevents infections by creating a sterile environment.
Discuss the hormonal changes that trigger childbirth.
- Childbirth is triggered by a complex interplay of hormonal signals, primarily involving oxytocin, prostaglandins, and relaxin. Oxytocin, released by the pituitary gland, stimulates uterine contractions. Prostaglandins, produced by the uterus, further enhance these contractions. Relaxin helps to soften the cervix and relax the pelvic ligaments, facilitating the passage of the baby through the birth canal.
How do modern contraceptive methods prevent pregnancy?
- Modern contraceptive methods prevent pregnancy through various mechanisms. Hormonal contraceptives, like birth control pills, inhibit ovulation and thicken cervical mucus to prevent sperm from reaching the egg. Barrier methods, such as condoms, physically block sperm from entering the uterus. Intrauterine devices (IUDs) prevent fertilization by altering the uterine environment. Sterilization procedures, like vasectomy and tubal ligation, provide permanent contraception by blocking the passage of sperm or eggs.
Explain the process and significance of lactation.
- Lactation is the process of milk production in the mammary glands, stimulated by the hormone prolactin. After childbirth, oxytocin causes the milk to be ejected from the breasts. Breast milk provides essential nutrients and antibodies to the newborn, supporting growth and immune protection during the early stages of life.
What are the ethical considerations surrounding assisted reproductive technologies?
- Assisted reproductive technologies (ART) raise ethical considerations related to the manipulation of human embryos, the potential for multiple pregnancies, the use of donor gametes, and the rights of the resulting children. There are also concerns about access to ART, the potential for exploitation, and the implications of genetic screening and selection.
How do hormonal imbalances affect the reproductive system?
- Hormonal imbalances can disrupt the normal functioning of the reproductive system, leading to issues such as irregular menstrual cycles, infertility, polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), and erectile dysfunction. These imbalances can result from various factors, including stress, illness, obesity, or endocrine disorders.
What is the importance of prenatal care in pregnancy?
- Prenatal care is essential for monitoring the health of both the mother and the fetus during pregnancy. Regular check-ups allow for early detection of potential complications, such as gestational diabetes, preeclampsia, or fetal abnormalities. Prenatal care also provides education on proper nutrition, exercise, and childbirth preparation, contributing to a healthy pregnancy and delivery.
Describe the development and function of the umbilical cord.
- The umbilical cord forms from the connection between the embryo and the placenta. It contains two arteries and one vein, encased in a protective layer of Wharton’s jelly. The umbilical cord transports oxygenated blood and nutrients from the placenta to the fetus while carrying waste products back to the placenta for disposal, serving as the lifeline between mother and baby during pregnancy.

Get involved!
Comments