
Download books 📚 chapter 6 Electromagnetic Induction
Important Questions and Answers
What is electromagnetic induction?
Answer: Electromagnetic induction is the phenomenon where an electromotive force (EMF) is induced in a conductor when it is exposed to a changing magnetic field.
Who discovered electromagnetic induction?
Answer: Electromagnetic induction was discovered by Michael Faraday in 1831.
What is Faraday’s law of electromagnetic induction?
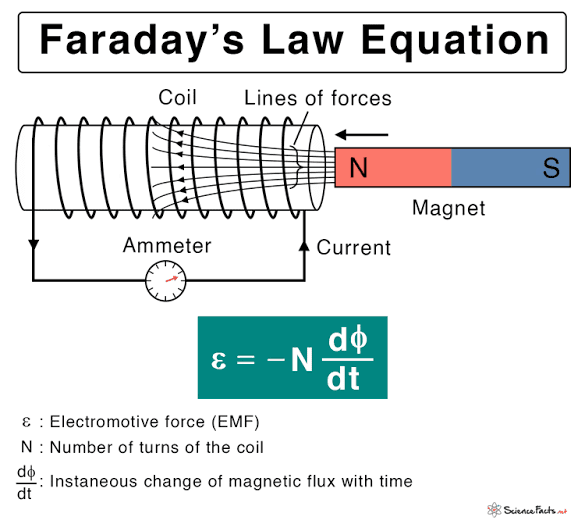
Answer: Faraday’s law states that the induced EMF in a circuit is directly proportional to the rate of change of magnetic flux through the circuit.
What is Lenz’s law?
Answer: Lenz’s law states that the direction of the induced EMF and hence the induced current in a circuit is such that it opposes the cause that produces it.
What is magnetic flux?
Answer: Magnetic flux is the product of the magnetic field and the area through which the field lines pass, considering the angle between the field lines and the normal to the area.
Why does an induced current oppose the change in magnetic flux?
Answer: According to Lenz’s law, the induced current produces a magnetic field that opposes the change in the original magnetic flux, thereby conserving energy.
What are the factors affecting the magnitude of induced EMF?
Answer: The magnitude of induced EMF depends on the rate of change of magnetic flux, the number of turns in the coil, and the strength of the magnetic field.
What is mutual induction?
Answer: Mutual induction is the process by which a change in the current in one coil induces an EMF in a neighboring coil.
What is self-induction?
Answer: Self-induction is the phenomenon where a change in current in a coil induces an EMF in the same coil.
What is the significance of the direction of induced current as per Lenz’s law?
Answer: The direction of the induced current as per Lenz’s law ensures that the induced EMF opposes the change in magnetic flux, thus obeying the law of conservation of energy.
What happens when a conductor moves perpendicular to a magnetic field?
Answer: When a conductor moves perpendicular to a magnetic field, an EMF is induced across its ends, causing a current to flow if the circuit is closed.
Can a steady magnetic field induce current in a stationary conductor?
Answer: No, a steady magnetic field cannot induce current in a stationary conductor because there is no change in magnetic flux.
What is the principle behind the working of a transformer?
Answer: The principle behind the working of a transformer is mutual induction, where a changing current in the primary coil induces a varying EMF in the secondary coil.
Why is Lenz’s law consistent with the principle of conservation of energy?
Answer: Lenz’s law is consistent with the conservation of energy because it ensures that the induced current opposes the change in magnetic flux, preventing the creation of energy from nothing.
What is eddy current?
Answer: Eddy currents are circular currents induced within conductors due to a changing magnetic field, which can cause heating and energy loss.
How can eddy currents be minimized in transformers?
Answer: Eddy currents can be minimized by using laminated cores in transformers, which reduces the loop area available for the currents.
What is the application of electromagnetic induction in power generation?
Answer: Electromagnetic induction is used in power generation where mechanical energy is converted into electrical energy by rotating a coil in a magnetic field.
Explain the role of electromagnetic induction in the working of an electric generator.
Answer: In an electric generator, mechanical energy is used to rotate a coil within a magnetic field, inducing an EMF according to Faraday’s law, which drives an electric current.
How does a changing magnetic field induce an electric field?
Answer: According to Faraday’s law, a changing magnetic field induces an electric field, which is manifested as an EMF in a conductor placed within the magnetic field.
What is the significance of Fleming’s right-hand rule in electromagnetic induction?
Answer: Fleming’s right-hand rule helps determine the direction of induced current when a conductor moves through a magnetic field. The thumb represents the direction of motion, the index finger the magnetic field, and the middle finger the direction of the induced current.
Class 12th physics Chapter 6 Electromagnetic Induction Handwritten note PDF download
👇👇👇👇👇👇
Faraday’s Laws of Electromagnetic Induction

Michael Faraday was a pioneering English scientist born on September 22, 1791, in Newington Butts, now part of London. He is best known for his contributions to the fields of electromagnetism and electrochemistry. Despite having little formal education, Faraday became one of the most influential scientists in history due to his natural curiosity and dedication to experimentation.
Faraday’s most significant work includes the discovery of electromagnetic induction, which led to the invention of the electric generator. This discovery, encapsulated in Faraday’s Laws of Electromagnetic Induction, is fundamental to modern technology, enabling the generation of electricity that powers homes, industries, and cities today. He also discovered the laws of electrolysis, which describe the chemical changes that occur when an electric current passes through a substance
Faraday’s research in magnetism led to the development of the concept of the magnetic field, a foundational idea in physics that describes the influence of magnets and currents on their surroundings. Additionally, he invented the Faraday cage, a device that shields its contents from external electric fields, which has important applications in various technologies.
Despite his immense contributions to science, Faraday remained humble and declined many honors, including a knighthood. He was also a deeply religious man and a member of the Sandemanian Church, which influenced his approach to life and work. Faraday passed away on August 25, 1867, leaving behind a legacy that continues to impact the world of science and technology.

Get involved!
Comments